As technology races forward, battery technology has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. From smartphones to electric vehicles, battery performance directly affects the endurance and user experience of our devices. Among the many battery technologies, prismatic and cylindrical cells are the two most common forms. Today, we delve into the characteristics of these two types of cells and compare their strengths and weaknesses in practical applications.
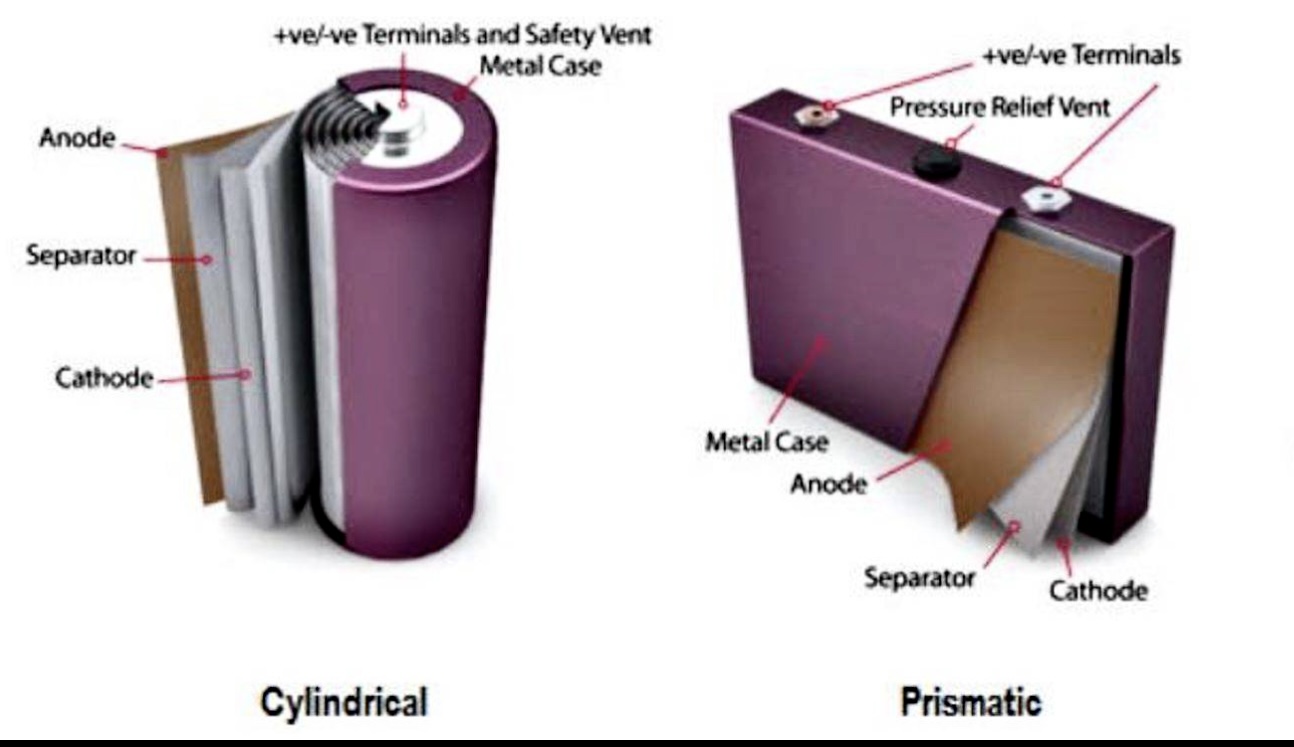
1. Differences in Shape and Structure
Prismatic cells, as the name suggests, are square in shape, which allows for higher space utilization within the battery, enabling more active material and thus increasing energy density. The casing of prismatic cells is usually made of aluminum plastic film or stainless steel, offering good sealing and mechanical strength.
Cylindrical cells are known for their classic cylindrical shape, a design that is more mature in battery manufacturing with more stable technology. The casing of cylindrical cells is usually made of steel or aluminum, providing good mechanical strength and impact resistance.
2. Energy Density Showdown
In terms of energy density, prismatic cells, due to their shape, can achieve higher space utilization, thus providing more electricity in the same volume. This is an important consideration for electronic products that pursue thin and light design and long battery life.
Cylindrical cells, although slightly inferior in space utilization, have a competitive edge in certain applications due to their mature manufacturing process and stable performance. For example, in devices that require fast charging and discharging, the high-rate discharge capability of cylindrical cells is a significant advantage.
3. Safety Considerations
Safety is a core issue in battery design. Prismatic cells, due to their structural characteristics, can reserve more safety space during design to cope with potential thermal runaway situations. Moreover, the aluminum plastic film casing of prismatic cells can expand to release pressure in case of failure, thereby reducing the risk of explosion.
Cylindrical cells also have strict safety design standards. Their steel or aluminum casing can resist internal pressure increases to some extent, but once thermal runaway occurs, the risk of explosion for cylindrical cells is relatively high. This is why cylindrical cells require a more sophisticated Battery Management System (BMS) to ensure safety.
4. Cost and Manufacturing Process Comparison
In terms of cost and manufacturing processes, cylindrical cells, due to their mature production lines and wide application, usually have lower production costs. This gives cylindrical cells a cost advantage in large-scale production.
Prismatic cells, although advantageous in energy density, have more complex manufacturing processes and higher production costs. However, with technological advancements, the production cost of prismatic cells is gradually decreasing, enhancing their market competitiveness.
5. Adaptability to Application Scenarios
In different application scenarios, prismatic and cylindrical cells each have their strengths. For example, in the field of electric vehicles, prismatic cells are favored for their high energy density and good safety performance. In contrast, in some small electronic devices, cylindrical cells are more popular due to their mature technology and cost advantages.
6. Future Development Trends
With the continuous advancement of battery technology, both prismatic and cylindrical cells are constantly being optimized and developed. Prismatic cells have great potential in increasing energy density and safety, while cylindrical cells have clear advantages in improving charge and discharge efficiency and reducing costs.
Conclusion:
Prismatic and cylindrical cells each have their strengths and weaknesses, and their selection depends on specific application needs and cost considerations. With technological progress, we can anticipate that both types of cells will play a greater role in their respective fields, jointly promoting the advancement of battery technology. As consumers, we look forward to enjoying safer, more efficient, and economical battery products, and as manufacturers, we need to continuously innovate and optimize to meet market demands. The competition between prismatic and cylindrical cells is not just a competition of shapes but also of technology and innovation. Let's wait and see who will dominate the battery market in the future.
Welcome to learn about Shenzhen Genchips Trading Limited, a thriving high-tech enterprise in the field of new energy. Since the establishment of the company, we have been committed to becoming a leader in the radio control model battery industry, providing customers with the highest quality products and services.
This article is from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.
As technology races forward, battery technology has become an indispensable part of our daily lives. From smartphones to electric vehicles, battery performance directly affects the endurance and user experience of our devices. Among the many battery technologies, prismatic and cylindrical cells are the two most common forms. Today, we delve into the characteristics of these two types of cells and compare their strengths and weaknesses in practical applications.

1. Differences in Shape and Structure
Prismatic cells, as the name suggests, are square in shape, which allows for higher space utilization within the battery, enabling more active material and thus increasing energy density. The casing of prismatic cells is usually made of aluminum plastic film or stainless steel, offering good sealing and mechanical strength.
Cylindrical cells are known for their classic cylindrical shape, a design that is more mature in battery manufacturing with more stable technology. The casing of cylindrical cells is usually made of steel or aluminum, providing good mechanical strength and impact resistance.
2. Energy Density Showdown
In terms of energy density, prismatic cells, due to their shape, can achieve higher space utilization, thus providing more electricity in the same volume. This is an important consideration for electronic products that pursue thin and light design and long battery life.
Cylindrical cells, although slightly inferior in space utilization, have a competitive edge in certain applications due to their mature manufacturing process and stable performance. For example, in devices that require fast charging and discharging, the high-rate discharge capability of cylindrical cells is a significant advantage.
3. Safety Considerations
Safety is a core issue in battery design. Prismatic cells, due to their structural characteristics, can reserve more safety space during design to cope with potential thermal runaway situations. Moreover, the aluminum plastic film casing of prismatic cells can expand to release pressure in case of failure, thereby reducing the risk of explosion.
Cylindrical cells also have strict safety design standards. Their steel or aluminum casing can resist internal pressure increases to some extent, but once thermal runaway occurs, the risk of explosion for cylindrical cells is relatively high. This is why cylindrical cells require a more sophisticated Battery Management System (BMS) to ensure safety.
4. Cost and Manufacturing Process Comparison
In terms of cost and manufacturing processes, cylindrical cells, due to their mature production lines and wide application, usually have lower production costs. This gives cylindrical cells a cost advantage in large-scale production.
Prismatic cells, although advantageous in energy density, have more complex manufacturing processes and higher production costs. However, with technological advancements, the production cost of prismatic cells is gradually decreasing, enhancing their market competitiveness.
5. Adaptability to Application Scenarios
In different application scenarios, prismatic and cylindrical cells each have their strengths. For example, in the field of electric vehicles, prismatic cells are favored for their high energy density and good safety performance. In contrast, in some small electronic devices, cylindrical cells are more popular due to their mature technology and cost advantages.
6. Future Development Trends
With the continuous advancement of battery technology, both prismatic and cylindrical cells are constantly being optimized and developed. Prismatic cells have great potential in increasing energy density and safety, while cylindrical cells have clear advantages in improving charge and discharge efficiency and reducing costs.
Conclusion:
Prismatic and cylindrical cells each have their strengths and weaknesses, and their selection depends on specific application needs and cost considerations. With technological progress, we can anticipate that both types of cells will play a greater role in their respective fields, jointly promoting the advancement of battery technology. As consumers, we look forward to enjoying safer, more efficient, and economical battery products, and as manufacturers, we need to continuously innovate and optimize to meet market demands. The competition between prismatic and cylindrical cells is not just a competition of shapes but also of technology and innovation. Let's wait and see who will dominate the battery market in the future.
Welcome to learn about Shenzhen Genchips Trading Limited, a thriving high-tech enterprise in the field of new energy. Since the establishment of the company, we have been committed to becoming a leader in the radio control model battery industry, providing customers with the highest quality products and services.
This article is from the internet. If there is any infringement, please contact us for removal.












