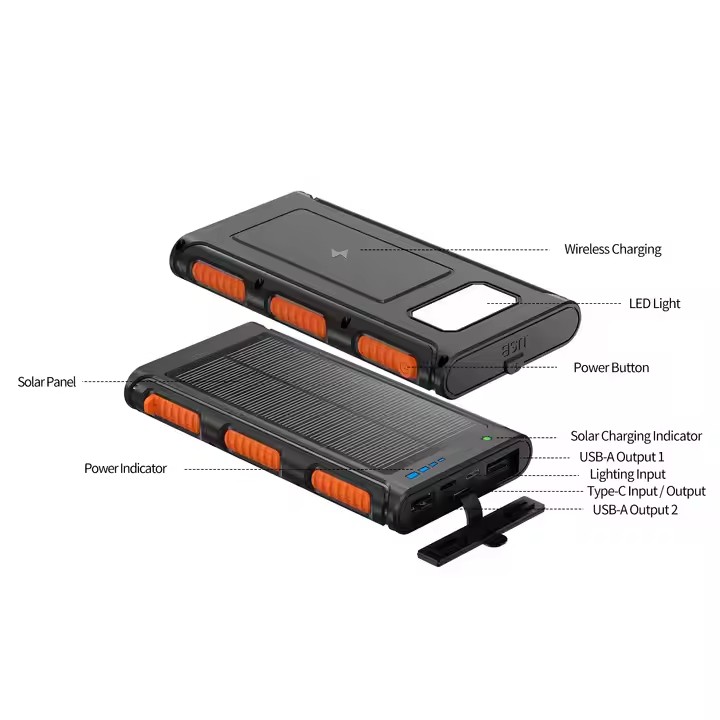
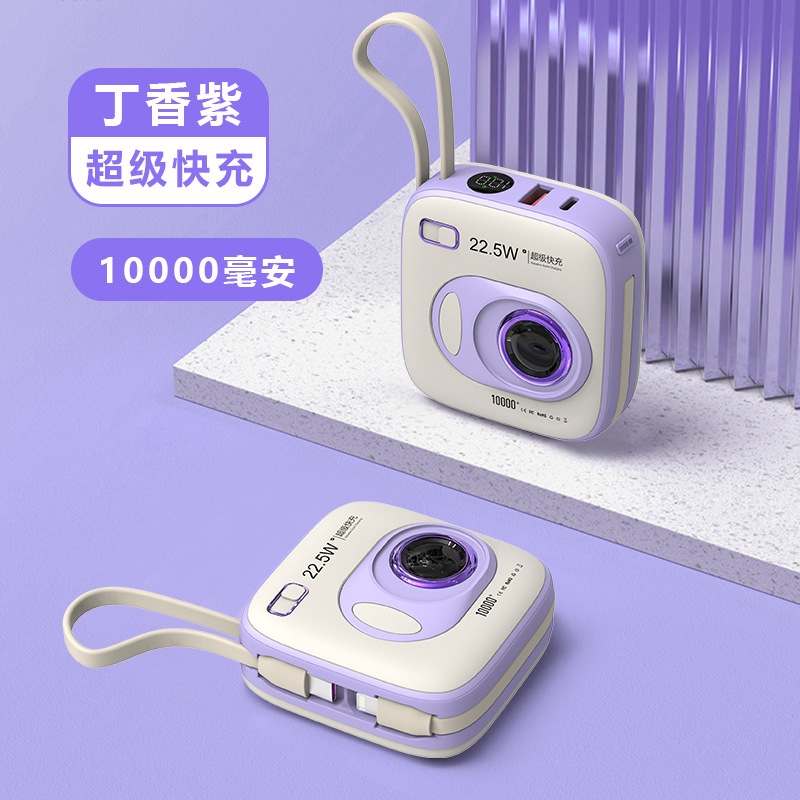
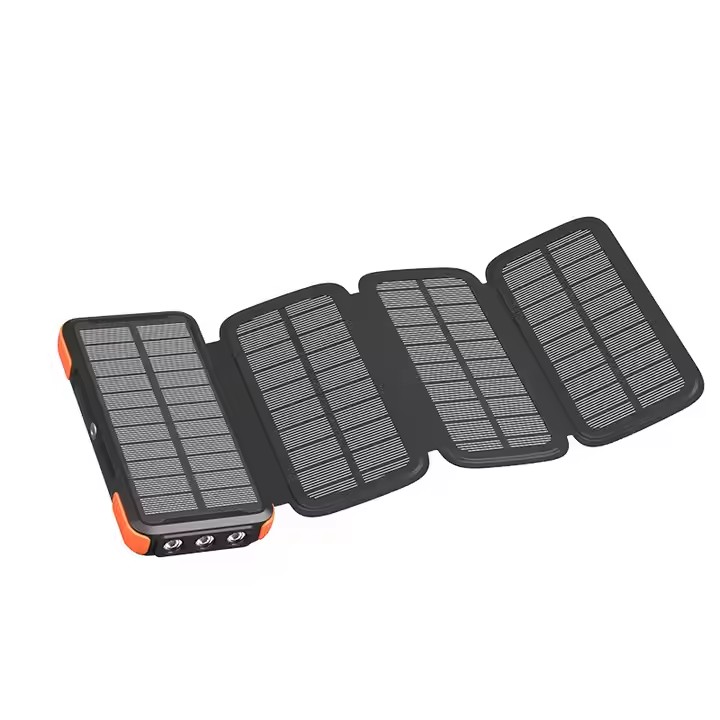
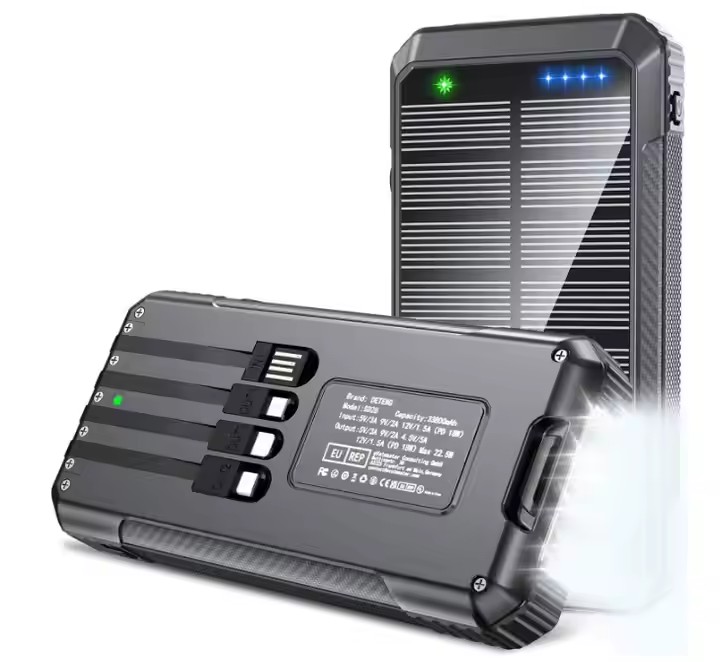
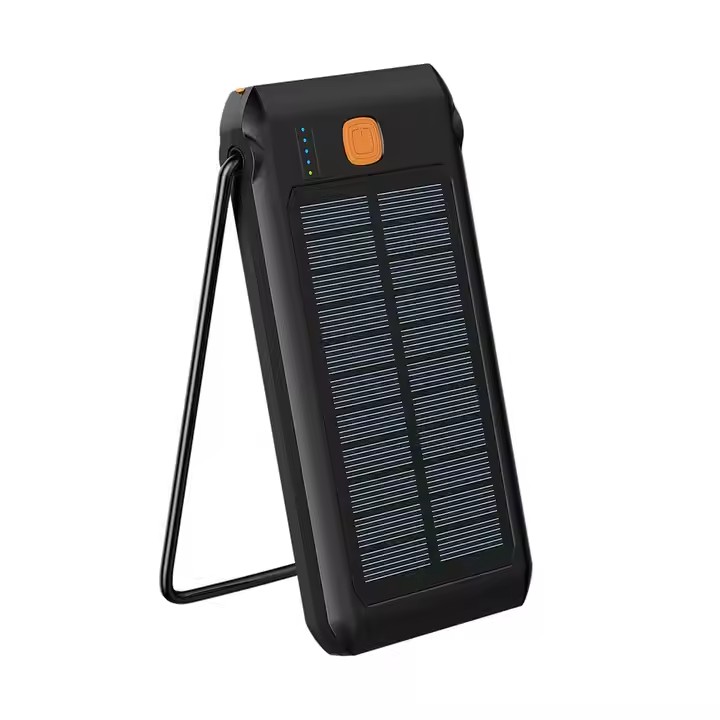
TUO-HY-2307
Multi Functional Solar Energy Power Bank High Capacity 10000mAH Strong Camping Lamp Waterproof Dustproof Power Banks
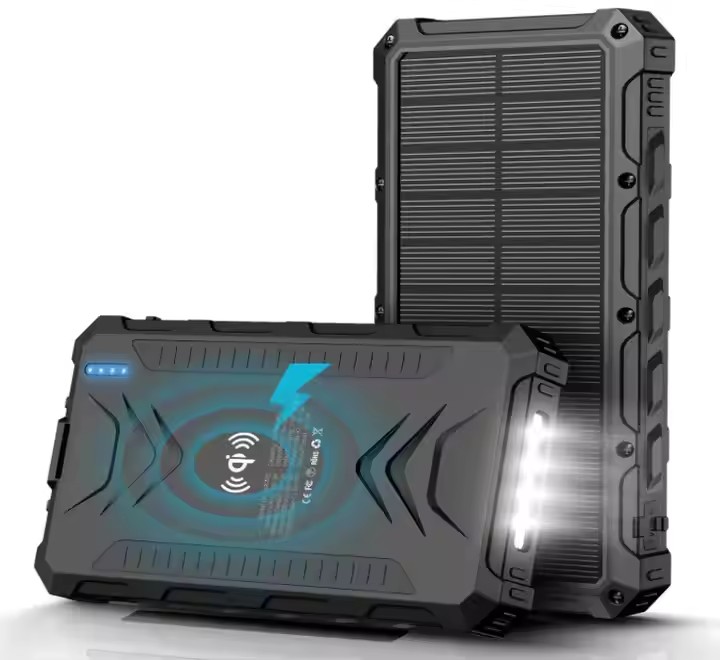

TUO-S26W
IP66 Waterproof Type C Power Bank 20000 Qc 3.0 Fast Charging Portable Solar Wireless Charger Pd Power Bank
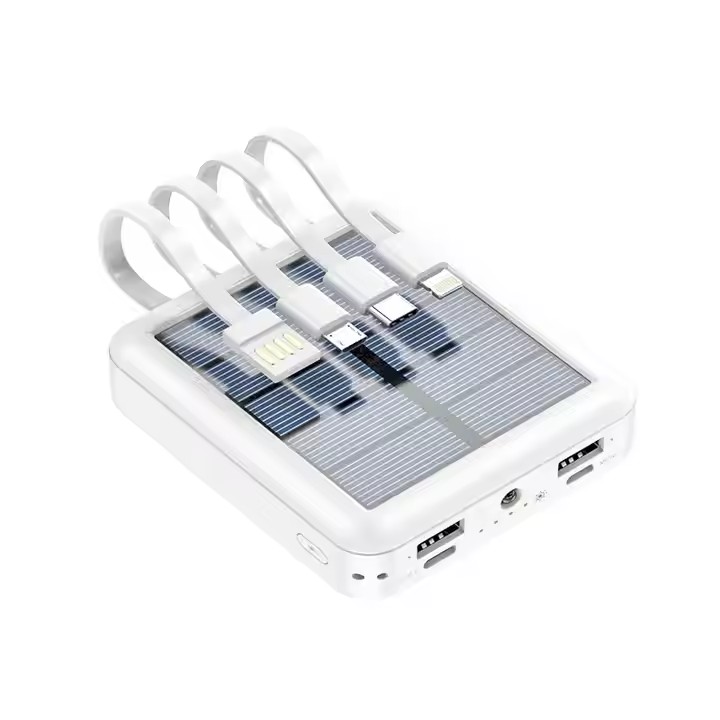

TUO-PB03
With Cable Solar Shared Four-wire Power Bank Large Capacity 20000 MAh Outdoor Mini Power Bank PB03
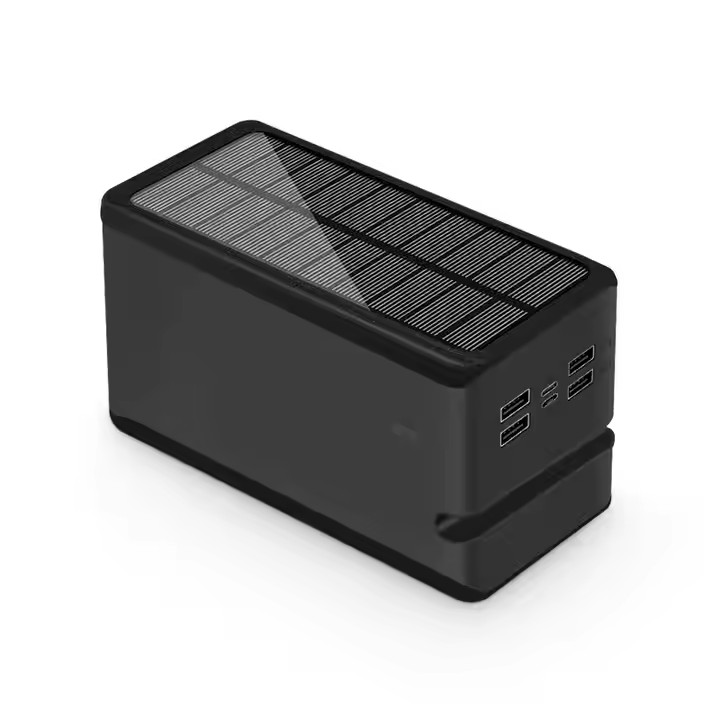

TUO-=PS-10+
Portable Camping Solar Power Bank 100000mah IP66 Waterproof 100000mah Solar Phone Charger
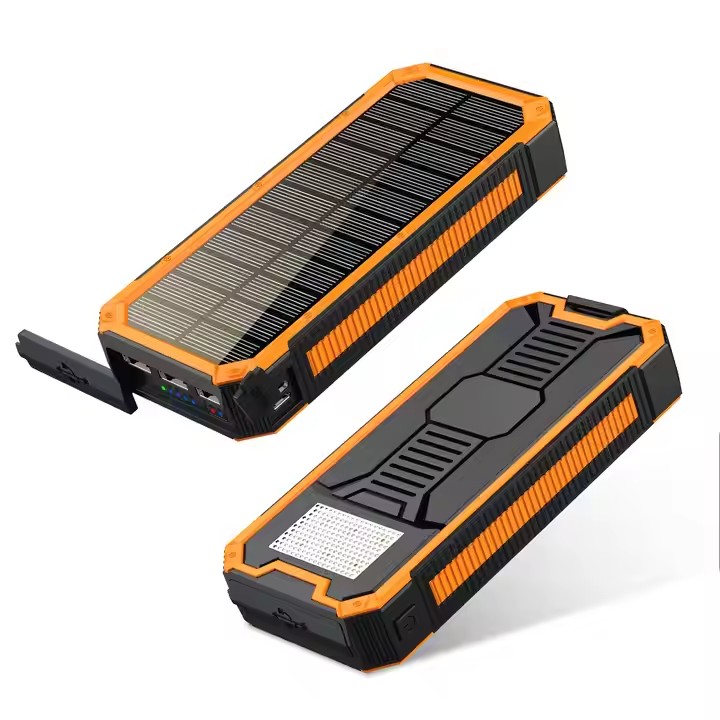

TUO-YD-888K
Free Sample New Product Creative 2025 Electronics 20000mAh Quick Charge Portable Waterproof High Capacity Solar Power Bank
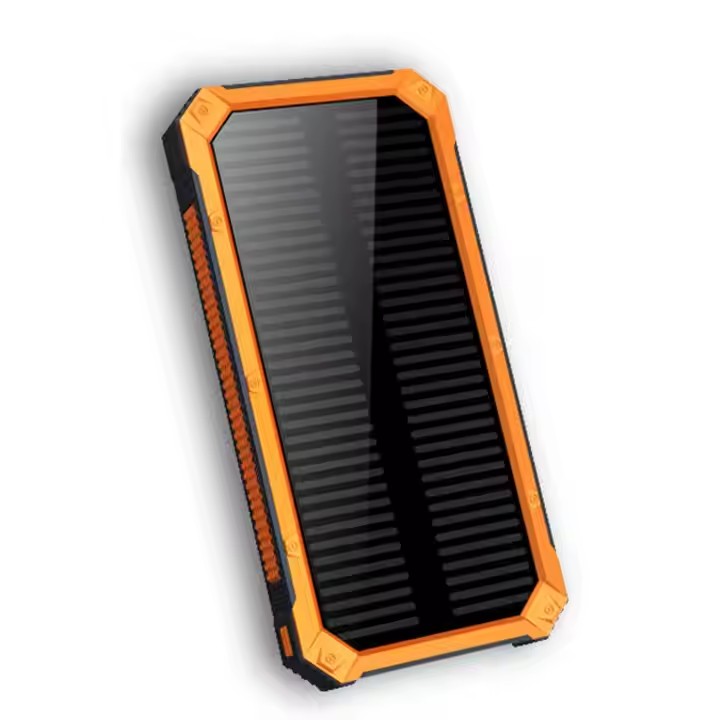

TUO-V9
High-Capacity 12000mAh Portable LED Flashlight Solar Power Bank Fast 2A Output Micro Compatible Lithium Battery DC Outdoor Usage
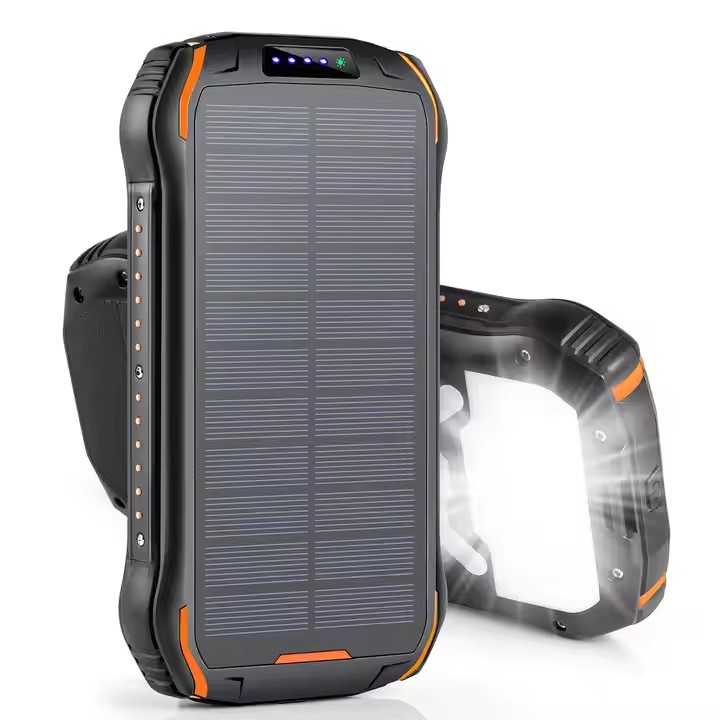

TUO-i26s
New Product Ideas 2025 Electronics Li-Polymer Battery Rechargeable Type-C Input and Output 26800mAh Solar Waterproof Power Bank

TUO-DO3
Portable Outdoor Trending Mobile Phone Fast Charging 20000Mah Waterproof Solar Panel Charger Powerbank Solar Power Bank
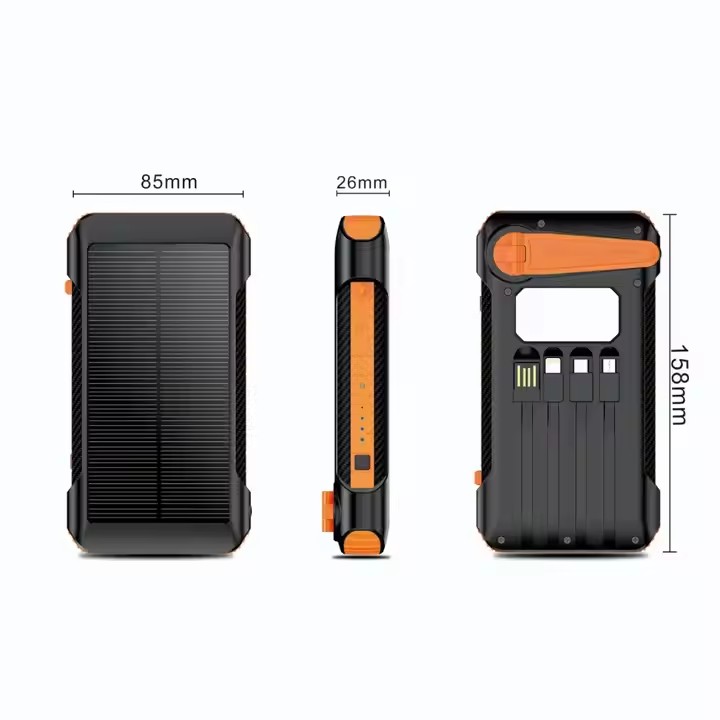

TUO-809024
Factory Wholesale Portable Manual Power Generation Solar Power Bank 30000mah 20000mah Waterproof Solar Charger Power Bank

TUO-DO2
Portable Outdoor Trending Mobile Phone Fast Charging 20000Mah Waterproof Solar Panel Charger Powerbank Solar Power Bank
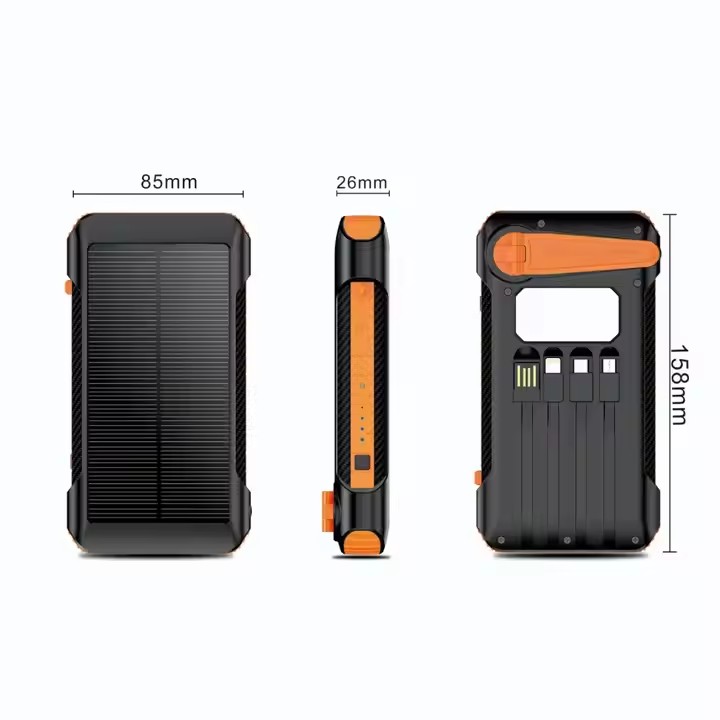

TUO-809024
Factory Wholesale Portable Manual Power Generation Solar Power Bank 30000mah 20000mah Waterproof Solar Charger Power Bank